Lightning Protection Standards in Vietnam and The World
- Overview of Lightning Protection Standards: Importance and Applications
- 1. Introduction
- 2. International Lightning Protection Standards
- 3. Continental Lightning Protection Standards
- 4. National Lightning Protection Standards
- 5. Vietnamese Lightning Protection Standards
- 6. Sector-Specific Lightning Protection Standards
- 7. Significance and Importance of Lightning Protection Standards
- Conclusion
TAEC - Lightning protection is an essential aspect of ensuring safety for buildings and electronic equipment. Adhering to lightning protection standards not only guarantees safety but also optimizes system efficiency. This article will guide you through international, continental, national, and Vietnamese lightning protection standards, highlighting their significance and practical applications in various sectors.
Overview of Lightning Protection Standards: Importance and Applications
1. Introduction
Lightning protection is a crucial aspect of ensuring safety for buildings and electronic equipment. Adhering to lightning protection standards not only guarantees safety but also optimizes the efficiency of the system. This article will list international, continental, national, and Vietnamese lightning protection standards, explaining their significance and importance.
2. International Lightning Protection Standards
-
IEC 62305: This standard by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) consists of four main parts:
- IEC 62305-1: General principles - provides an overview of lightning protection, explaining the basic concepts and components of the system.
- IEC 62305-2: Risk management - guides on how to assess and calculate the risks posed by lightning to structures.
- IEC 62305-3: Physical damage to structures and life hazard - details requirements for the design and installation of lightning protection systems to safeguard structures and people.
- IEC 62305-4: Electrical and electronic systems within structures - provides measures to protect electrical and electronic systems from lightning electromagnetic impulses.
-
NFPA 780: This standard by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) in the United States covers lightning protection systems. It includes detailed guidelines for the design, installation, and maintenance of lightning protection systems for both residential and industrial structures.
-
IEEE 998: This standard by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) focuses on the design of lightning protection systems for structures and electrical systems. It concentrates on methods and techniques for designing lightning protection systems for power and industrial facilities.
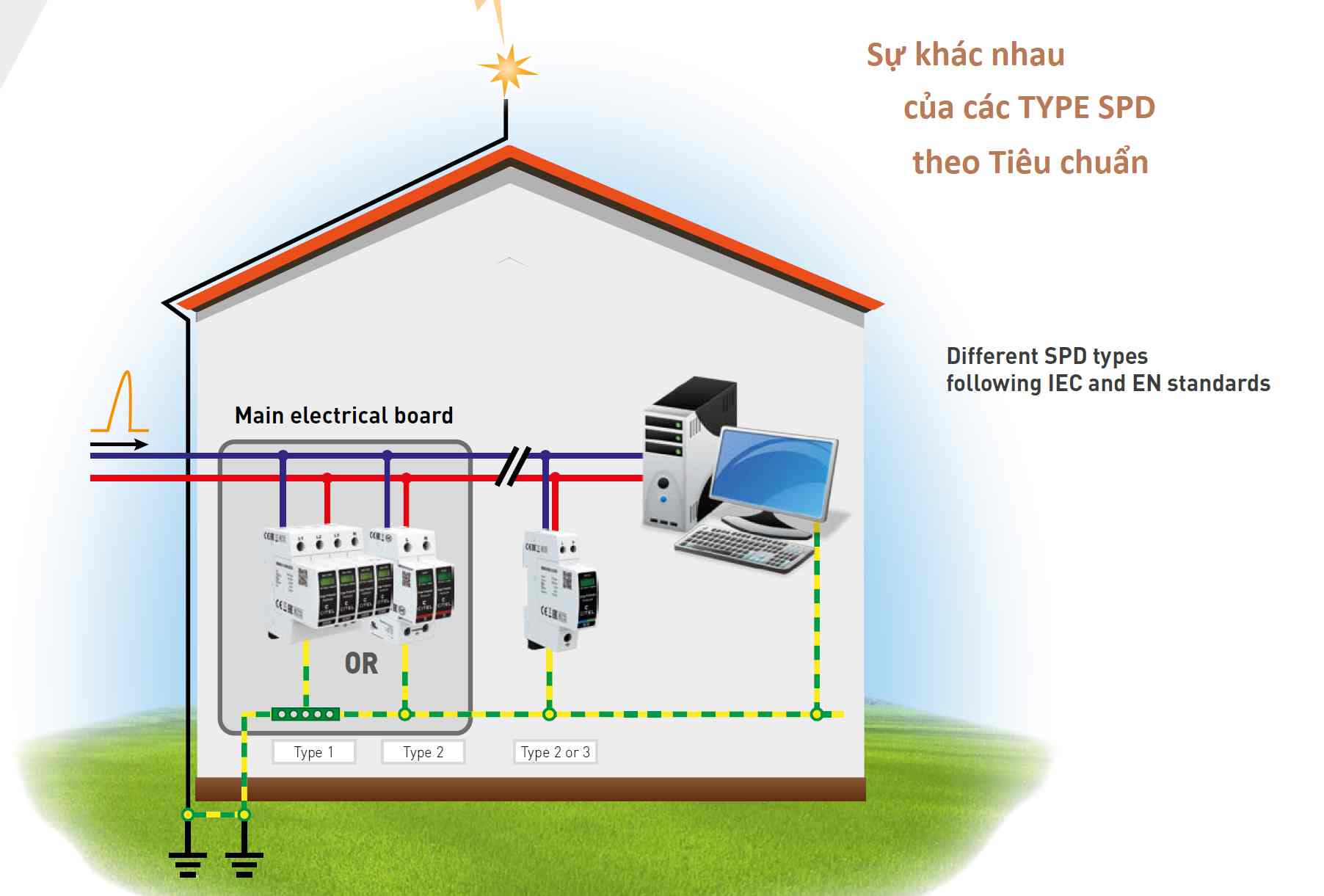
- EC 61643: This standard focuses on Surge Protective Devices (SPD). It defines various types of SPDs and outlines their installation and usage to protect electrical and electronic systems from surge overvoltages.
- IEC 61662: This standard provides a methodology for assessing the risks posed by lightning, helping to determine appropriate protective measures.
3. Continental Lightning Protection Standards
-
Europe:
- EN 62305: The European standard, equivalent to IEC 62305, is applied in EU member countries.
- This standard ensures uniform lightning protection across Europe, helping structures comply with international regulations.
-
Asia:
- JIS A 4201: The Japanese standard for lightning protection of buildings. It specifies requirements for the design, installation, and maintenance of lightning protection systems for buildings in Japan.
- GB 50057: The Chinese standard for lightning protection of buildings. Provides detailed guidance on lightning protection measures, including the design and inspection of systems.
4. National Lightning Protection Standards
-
United States:
- NFPA 780 and UL 96 (Underwriters Laboratories): Both standards provide detailed requirements for lightning protection, including design, installation, and maintenance.
-
United Kingdom:
- BS EN 62305: This standard, equivalent to IEC 62305, ensures that structures in the UK comply with international lightning protection regulations.
-
Australia:
- AS/NZS 1768: The Australian and New Zealand standard for lightning protection of structures and electrical systems. Specifies protection methods, design, and installation of lightning protection systems.
-
Canada:
- CAN/CSA-B72: The Canadian standard for lightning protection of structures. Includes requirements for the design, installation, and maintenance of lightning protection systems.
-
France:
- NF C 17-102: The French standard for lightning protection systems. It provides guidelines on the design, installation, and maintenance of lightning protection systems, focusing on both traditional and early streamer emission (ESE) systems.
-
Spain:
- UNE 21186: The Spanish standard for lightning protection systems. This standard includes guidelines for the design, installation, and maintenance of lightning protection systems, with a particular emphasis on early streamer emission (ESE) systems.
5. Vietnamese Lightning Protection Standards
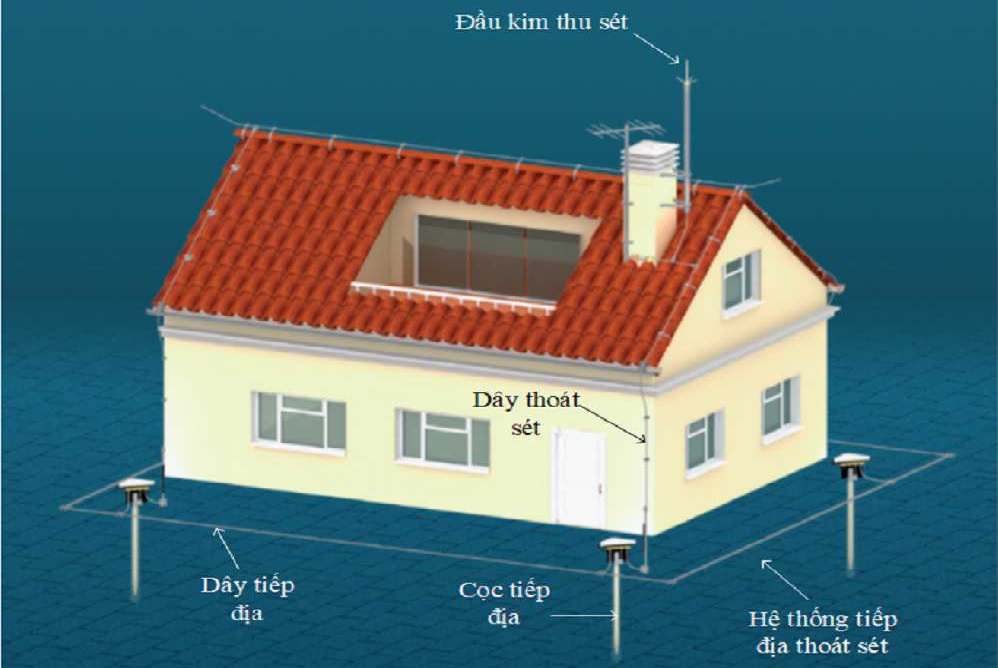
- TCVN 9385:2012: The national standard for lightning protection of buildings, based on IEC 62305. This standard specifies:
- Protection principles.
- Risk assessment.
- Design and installation of lightning protection systems.
- Protection of electrical and electronic systems.
The Standards - UL and IE
6. Sector-Specific Lightning Protection Standards
-
Oil and Gas Facilities:
- API RP 545: The American Petroleum Institute (API) standard for lightning protection of aboveground storage tanks. Specifies design and installation requirements to prevent lightning-induced fires and explosions.
-
Telecommunications:
- TIA-222: The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) standard for the construction and protection of telecommunication facilities from lightning. Specifies design and installation requirements for lightning protection systems for telecom facilities to ensure safety and maintain communication operations.
- TCVN 8071:2009: Telecommunication plant - Code of practice for lightning protection and earthing
-
Electric Power Industry:
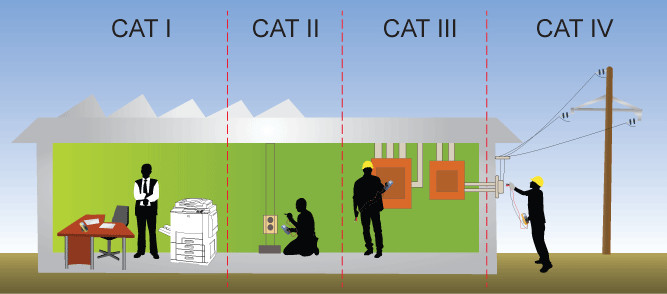
- IEC 60071: The International Electrotechnical Commission standard for insulation coordination in power systems. Specifies requirements for protecting power systems from lightning-induced overvoltages.
- IEEE C62: The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers standard for surge protection and overvoltage protection in power systems. Provides guidelines for protecting power systems from lightning and other overvoltage sources.
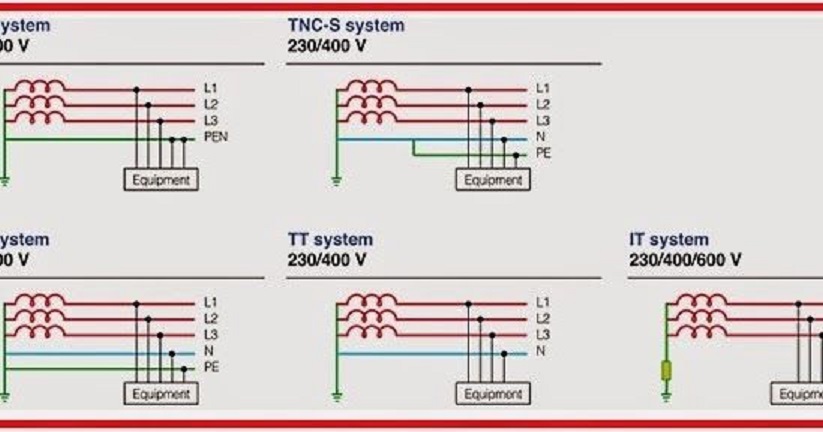
- TCVN 7447-4-41:2010: The national standard for Low-voltage electrical installations
-
Aviation:
- FAA-STD-019: The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) standard for protecting aviation facilities from lightning. Specifies requirements for the design and installation of lightning protection systems for airports and aviation facilities, ensuring safety for aircraft and passengers.
7. Significance and Importance of Lightning Protection Standards
- Ensuring Safety: Lightning protection standards help protect people, property, and equipment from the harmful effects of lightning. Adherence to these standards minimizes the risk of fires and damages.
- Enhancing System Efficiency: Standards provide specific guidelines for design and installation, helping lightning protection systems operate more efficiently.
- Legal Compliance: Compliance with lightning protection standards is a legal requirement in many countries. Non-compliance can result in penalties and legal liabilities.
- Cost Savings: By minimizing lightning-induced damages, lightning protection standards help save costs on repairs and replacements.
- Increasing Reliability: Standards ensure that lightning protection systems are correctly designed and installed, enhancing the reliability and lifespan of the system.
Conclusion
International, regional, and national lightning protection standards play a crucial role in safeguarding people and property from the adverse effects of lightning. Adhering to these standards ensures safety and optimizes the efficiency and reliability of lightning protection systems. The Vietnamese standard, TCVN 9385:2012, is a prime example of applying international standards to local conditions, providing tangible benefits for domestic construction projects. Sector-specific standards further enrich the overall system, ensuring safety and efficiency in specialized fields such as oil and gas, telecommunications, electric power, and aviation.