What is the Type of Surge Protective Devices (SPD)?
Surge Protective Devices (SPD) come in various types, each designed to meet specific standards such as IEC or UL. This article explains the different types of SPDs, their classifications, and a detailed comparison based on IEC and UL standards. Understanding these types will help you select the right SPD for your electrical system.
1. What is the Type of Surge Protective Devices (SPD)?
The Type of Surge Protective Devices (SPD) is a classification method used to categorize devices that protect electrical systems from voltage surges, based on their protection functions, installation locations, and the ability to withstand various surge currents. SPDs are classified according to two major standards: IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) and UL (Underwriters Laboratories). Each standard has its own classification and requirements to ensure the devices protect electrical systems from surge-related incidents.
2. Type of Surge Protective Devices According to IEC Standard
The IEC 61643-11 standard specifies performance requirements and testing methods for SPDs used in AC power systems. According to this standard, SPDs are classified into three main types with the following characteristics:
-
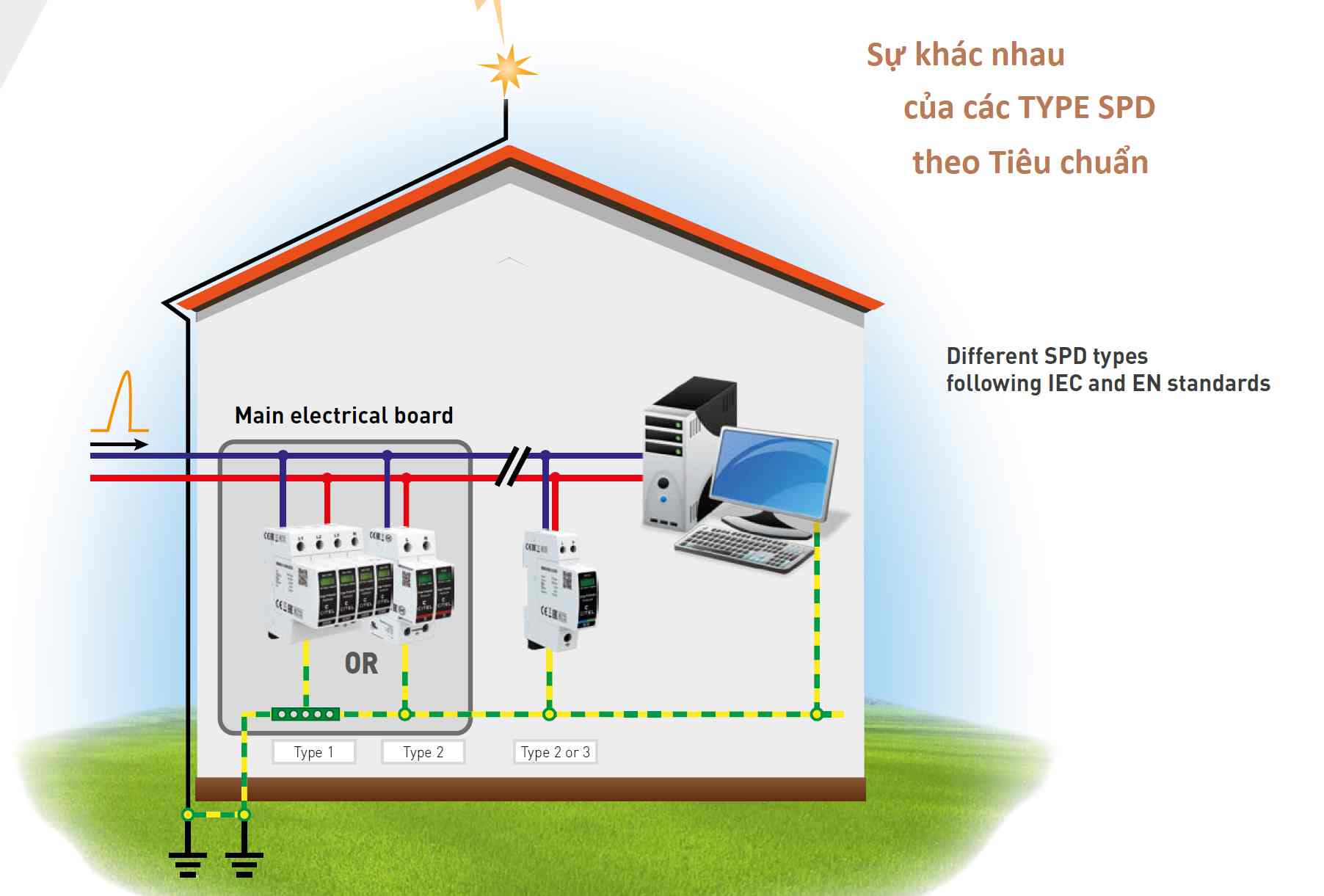
Type 1 SPD (Class I):
- Function: Protects the electrical system from direct lightning strikes.
- Installation Location: Installed at the system entrance, near the main distribution panel.
- Surge Waveform: 10/350 µs. This waveform simulates direct lightning strikes, with a rise time to peak in 10 µs and a decay to 50% in 350 µs.
- Surge Current Withstand (Iimp): High, typically from 10 kA upwards.
- Nominal Discharge Current (In): From 10 kA upwards, according to IEC 61643-11, Class I. This is the current the SPD can withstand multiple times without damage.
- Voltage Protection Level (Up): From 1.5 kV to 2 kV. Up is the maximum voltage the SPD allows to pass during discharge.
- Applications: Suitable for high-rise buildings, industrial facilities, and areas with a high risk of lightning strikes.
-
Type 2 SPD (Class II):
- Function: Protects the electrical system from surge voltages caused by indirect lightning strikes or switching operations.
- Installation Location: Installed at sub-distribution panels or after a Type 1 SPD.
- Surge Waveform: 8/20 µs. This waveform simulates surge voltages propagated within the electrical system, with a rise time to peak in 8 µs and a decay to 50% in 20 µs.
- Nominal Discharge Current (In): Medium, typically from 5 kA to 20 kA. This is the current the SPD can withstand multiple times without damage.
- Voltage Protection Level (Up): From 1.5 kV to 2 kV. Up is the maximum voltage the SPD allows to pass during discharge.
- Applications: Suitable for commercial, residential areas, and regions with moderate lightning risk.
-
Type 3 SPD (Class III):
- Function: Protects sensitive electronic equipment from residual surge voltages after they have been attenuated by Type 1 and Type 2 SPDs.
- Installation Location: Installed near sensitive electronic equipment such as sockets, small distribution boards, or terminal devices.
- Surge Waveform: 8/20 µs and 1.2/50 µs. These waveforms simulate residual surges, with faster rise times (1.2 µs) and slower decay times (50 µs).
- Nominal Discharge Current (In): Low, typically less than 5 kA.
- Voltage Protection Level (Up): From 1 kV to 1.5 kV. Up is the maximum voltage the SPD allows to pass during discharge.
- Applications: Suitable for sensitive electronic devices such as computers, telecommunication devices, and medical equipment.
3. Type of Surge Protective Devices According to UL Standard
The UL 1449 standard specifies requirements for SPDs used in electrical systems in North America. According to this standard, SPDs are classified into four Types:
-
Type 1 SPD:
- Function: Protects against surge voltages caused by direct or nearby lightning strikes from outside the electrical grid.
- Installation Location: Installed before the electricity meter, either before or after the main circuit breaker.
- Surge Current Withstand: Designed to withstand high surge currents.
- Applications: Suitable for large industrial and commercial buildings.
-
Type 2 SPD:
- Function: Protects against surge voltages propagated within the system or from the electrical grid.
- Installation Location: Installed after the main circuit breaker or at sub-distribution panels.
- Surge Current Withstand: Designed to withstand surge currents from the power grid or internal system faults.
- Applications: Suitable for residential and commercial areas.
-
Type 3 SPD:
- Function: Protects sensitive electronic devices from residual surge voltages.
- Installation Location: Installed at electrical outlets or near sensitive devices.
- Surge Current Withstand: Designed to withstand residual surge currents after passing through Type 1 and Type 2 SPDs.
- Applications: Suitable for household and office electronic devices.
-
Type 4 SPD:
- Function: Modular or assembly SPDs integrated into electrical equipment.
- Installation Location: Typically integrated within devices or distribution boards.
- Surge Current Withstand: Designed to meet the requirements of integrated electrical equipment.
- Applications: Suitable for electrical devices with built-in SPDs.
4. Comparison of SPD Types
| Criteria | Type 1 (IEC 61643-11) | Type 2 (IEC 61643-11) | Type 3 (IEC 61643-11) | Type 1 (UL 1449) | Type 2 (UL 1449) | Type 3 (UL 1449) | Type 4 (UL 1449) |
| Main Function | Protect against direct lightning strikes | Protect against propagated surges | Protect sensitive equipment | Protect against surges from the grid before the breaker | Protect against surges from the grid after the breaker | Protect sensitive equipment at the outlet | Integrated module within electrical equipment |
| Installation Location | System entrance | Sub-distribution panel | Near sensitive electronics | Before the electricity meter | After the main circuit breaker | At electrical outlets or near sensitive equipment | Integrated within electrical equipment |
| Surge Waveform | 10/350 µs | 8/20 µs | 8/20 µs or 1.2/50 µs | Not specifically defined | Not specifically defined | Not specifically defined | Not specifically defined |
| Surge Current Withstand | High (≥ 10 kA) | Medium (5-20 kA) | Low (< 5 kA) | High | Medium | Low | Depends on integrated equipment |
| Applications | Industrial, high-rise buildings | Commercial, residential | Sensitive electronics | Large industrial, commercial buildings | Residential, commercial | Household, office electronics | Electrical devices with integrated SPDs |
5. Conclusion
Selecting the correct type of surge protective device and understanding their classifications according to IEC and UL standards is crucial to ensuring that your electrical systems and electronic devices are adequately protected from voltage surges. Each standard provides a different approach to safeguarding electrical systems, depending on the specific requirements of the application and location.